Shaping Safer Road Policy

We need a strong policy framework and ambitious global targets if we are to deliver safer roads that save people’s lives.
iRAP and its partners are working with international bodies, national governments and highways agencies to build a global policy consensus for safer roads.
In 2015, the United Nations included halving road deaths and serious injuries as a Sustainable Development Goal (3.6). This game-changing move put road deaths centre stage – where they belong – as a global development issue, alongside poverty reduction targets and the right to clean water.
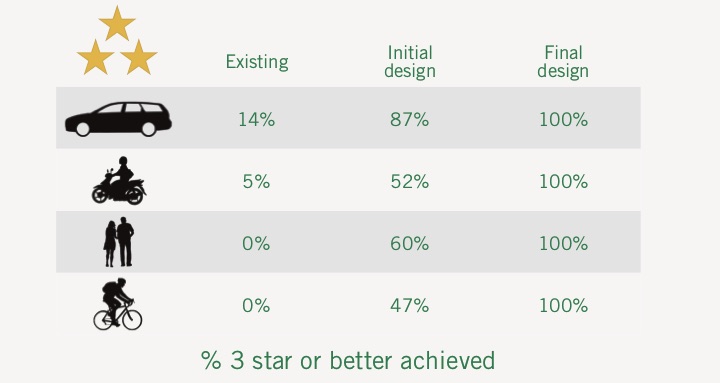
Now, the challenge is to build on this momentum. The UN Secretary General has recommended all new roads should be built to a 3-star or better standard and existing roads upgraded. The establishment of a Safer Roads Fund to maximise travel on 3-star or better roads can provide international finance institutions, health organisations, treasury officials, road executives and road builders with the social and economic basis for safer, sustainable roads.
Let’s work together to create a world free of high-risk roads and save lives!